Abstract
Introduction: Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a heterogeneous autoimmune disease characterized by autoantibody-mediated platelet destruction and impaired platelet production, resulting in thrombocytopenia and high bleeding risk. In patients with ITP, response to therapies has been challenging to predict, as neither durable responses nor long-term remissions are guaranteed. To date, there are several ITP therapies with varying efficacy and safety, but few predictive markers exist. Consequently, predicting the response to current therapies is crucial because it helps optimize the use of current and future therapies. Data from the ongoing, global phase 1/2 study (NCT03395210) provide evidence that rilzabrutinib, a Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor specifically developed to treat autoimmune disorders, could be a safe and efficacious treatment for patients with ITP. The aim of this report was to identify baseline factors that may predict response to treatment with rilzabrutinib in patients enrolled in the phase 1/2 ITP trial.
Methods: A total of 11 baseline clinical variables and pharmacokinetics (PK) exposure at steady-state were selected as potential predictors of platelet response among 45 patients who initiated 400 mg rilzabrutinib twice daily (BID). Platelet response was defined as ≥2 consecutive platelet counts of ≥50x109/L, separated by ≥5 days, and an increase from baseline of ≥20x109/L without the use of rescue medication during the 4 weeks before the latest elevated platelet count, and early response was defined as having platelet counts ≥50×109/L by day 8. Clinical predictors were selected based on clinical considerations anticipated to be associated with platelet response and evaluated by univariate logistic regression models. For continuous variables, the t test was used to test for differences, whereas for categorical variables, the Fisher exact test was used. PK exposure at steady-state was estimated based on post hoc analysis from a previously established population PK model.
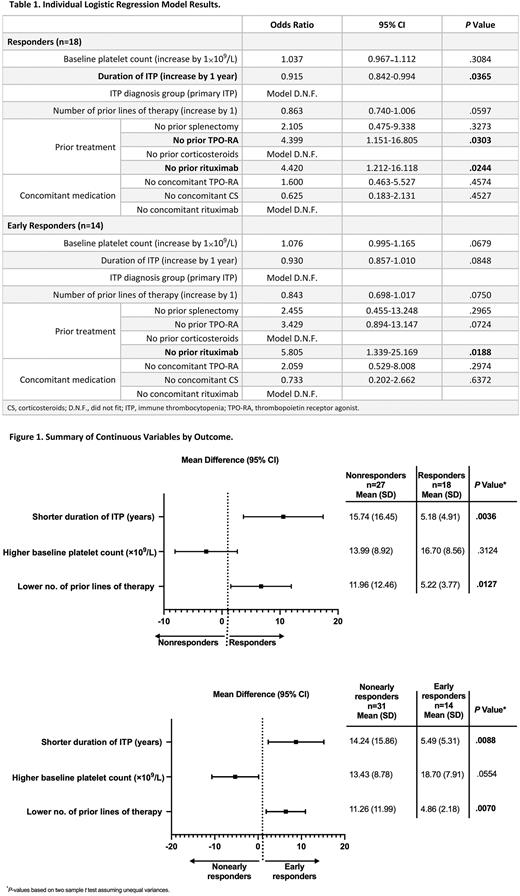
Results: Of the 45 patients who initiated 400 mg BID rilzabrutinib, 18 achieved the primary platelet response, of whom 14 were early responders. Significant predictors of response to rilzabrutinib, based on the univariate logistic regression models, were shorter duration of ITP (P=.04) and no prior use of thrombopoietic receptor agonists (TPO-RA; P=.03) or rituximab (P=.02; Table 1). No prior rituximab therapy was also a significant predictor in early responders (P=.02; Table 1). Conversely, the use of concomitant ITP medication with TPO-RA or corticosteroids was not associated with predicting either response or early response to rilzabrutinib treatment. Similar results were noted upon assessment of continuous variables by mean difference. Compared with their counterparts, responders had a significantly shorter mean duration of ITP (P<.01) and lower number of prior lines of therapy (P=.01) as did the early responders (P<.01 for both; Figure 1). Across categorical variables assessed by comparing proportions of patients, significant associations with being a responder vs nonresponder were seen with no prior use of TPO-RA (P=.05) and lack of prior rituximab therapy (P=.03). Responders accounted for 29% vs 64% of patients with vs without prior TPO-RA and 23% vs 57% of those with vs without prior rituximab. No prior rituximab was also significantly associated with early response (P=.02) to rilzabrutinib, with 48% of these patients being early responders vs 14% of those who received prior rituximab. None of the PK exposure metrics significantly impacted response to rilzabrutinib.
Conclusion: In heavily pretreated patients with ITP, the strongest predictors of response were short duration of ITP and no history of rituximab therapy, suggesting that patients who are more treatment naïve are more likely to respond to rilzabrutinib therapy than those receiving prior ITP medication. Nevertheless, interpretation of these observations should be caveated by their exploratory nature and the small sample size.
Disclosures
Kuter:Shionogi: Consultancy; CRICO: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; Genzyme: Consultancy; Takeda (Bioverativ): Consultancy, Research Funding; Protalex: Consultancy, Research Funding; argenx: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Alnylam: Consultancy, Research Funding; Agios: Consultancy, Research Funding; Actelion (Syntimmune): Consultancy, Research Funding; Caremark: Consultancy; BioCryst: Consultancy, Research Funding; UCB: Consultancy, Research Funding; Momenta: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Merck Sharp & Dohme: Consultancy; Kyowa Kirin: Consultancy; Rigel: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy; Principia: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Immunovant: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kezar: Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Dova: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Platelet Disorder Support Association: Consultancy; Platelet Biogenesis: Consultancy; Cellularity: Consultancy; Rubius: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Shire: Consultancy; Up-To-Date: Consultancy; Zafgen: Consultancy; Cellphire: Consultancy; Hengrui: Consultancy. Ghanima:Novartis, Amgen, Sobi, Argenx, UCB, Grifols, Bayer, Hutchmend, Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel and Accommodations, Research Funding. Khan:Seattle Children's Hospital: Ended employment in the past 24 months; Sanofi: Current Employment, Current equity holder in private company. Li:Sanofi: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company. Shan:Sanofi: Current Employment. Daak:Sanofi: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Cooper:Sanofi, Principia, Novartis, Griffols, Sobi, Argenyx, UCB, Rigel: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Rilzabrutinib is an investigational therapy being evaluated in a clinical study for the treatment of patients with immune thrombocytopenia.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal